Pharmacological actions
Again we may have same question as we have seen with directly acting agents.
They act on both. As they does not act directly instead they act indirectly by increasing acetylcholine levels which act on both muscarinic and nicotinic receptors.
So whatever the pharmacological actions we have seen with directly acting agents are again shown by these agents with additional nicotinic actions. Let’s see one by one.
Muscarinic actions
As we have already discussed the reason behind each pharmacological in previous section, here we will list out their actions.
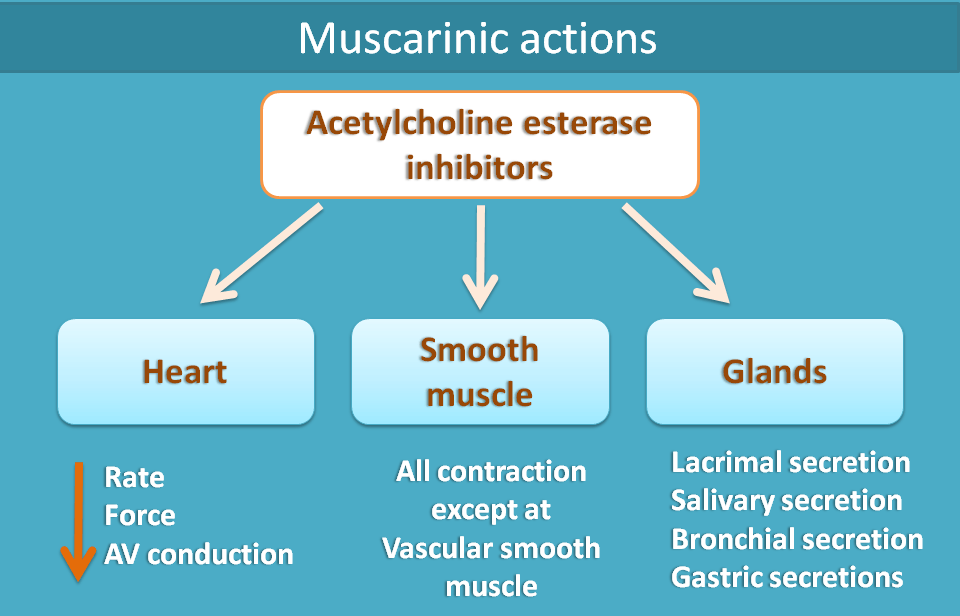
Heart
- Decrease in rate of contraction leading to bradycardia
- Decrease in force of contraction
- Decrease in AV conduction
Smooth muscle
All smooth muscle are contracted except vascular smooth muscle.
- Bronchoconstriction
- Increase in GI motility
- Bladder constriction
- Eye
- Pupilary constriction
- Ciliary muscle contraction
- Fall in intraocular pressure
Glands
- Lacrimal secretion
- Bronchial secretion
- Salivary secretion
- Sweat secretion
Nicotinic actions
Here they show marked differences with directly acting agents. Many of these agents have significant action on nicotinic receptors particularly at skeletal muscle.
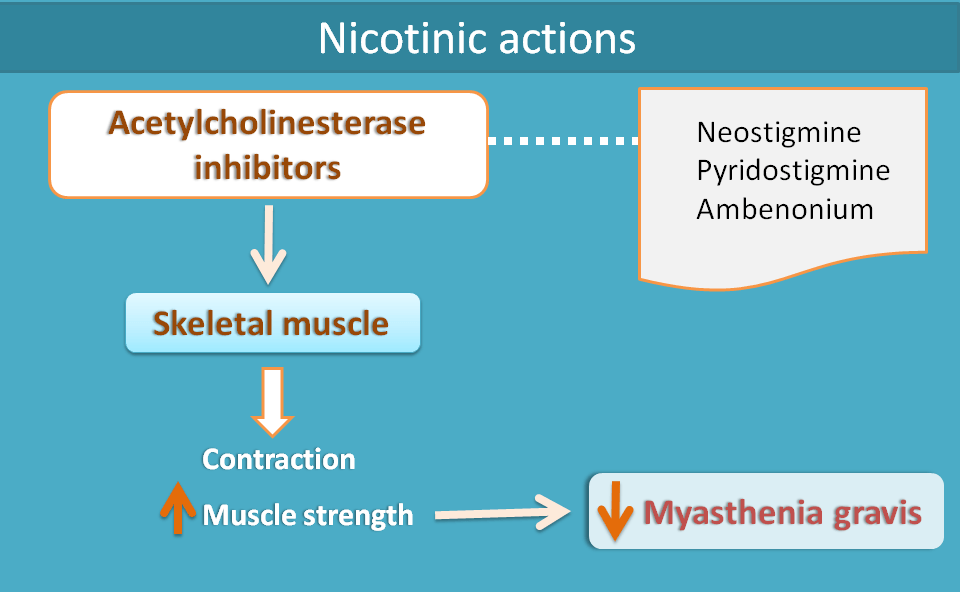
At the neuromuscular junction, acetylcholine is released by calcium mediated exocytosis which then acts on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors to open sodium channels leading to depolarisation followed by contraction. So, the extent of muscle contraction depends on the relative levels of acetylcholine at synaptic cleft which is highly effected by its rapid metabolism with ACh esterase.
The levels of ACh at neuromuscular junction is highly influenced by its rapid metabolism with Ach esterase
Hence acetylcholinesterase inhibitors increase ACh levels at neuromuscular junction and therby increase skeletal muscle contraction which is highly useful in myasthenia gravis.