Phenothiazines- Mechanism, side effects and uses
by egpat 06 Aug 2019
Phenothiazines are one class of typical antipsychotics that are indicated for schizophrenia. This chemical class contains many medications and most of them can be identified with various suffixes like either promazaine or phenazine. Interestingly, this group of compounds can also be used to treat emesis and allergic conditions. So let’s go with discussion of how they act and what the side effects they produce.
Chemical nature of phenothiazines
Chemically these are drugs with three cyclic rings with a side chain at 10th position. One of the important aspect in the chemistry of phenothiazines is the nature of their side chain, based on which they are classified further into three categories such as those with alkyl, piperidinyl and piperazinyl side chains.
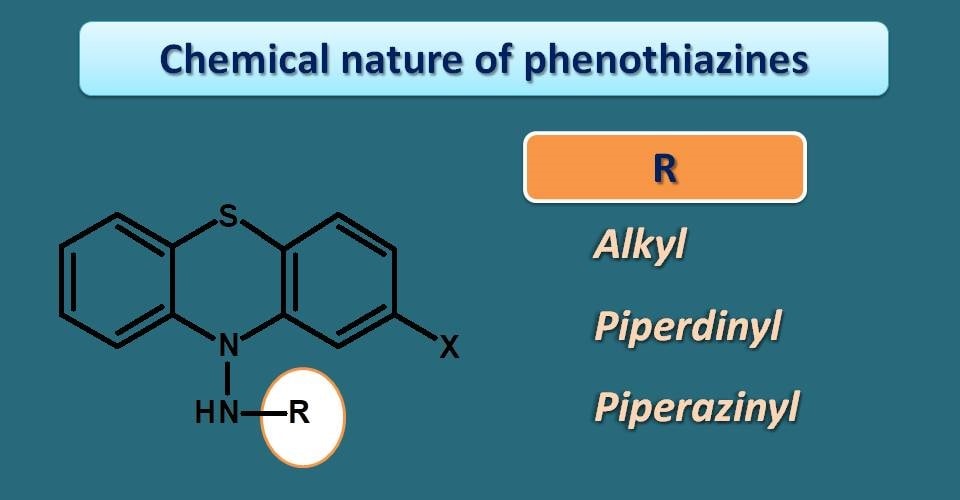
Drugs in these subcategories are as follows.
- Alkyl side chain
- Chrlopromazine
- Trifluopromazine
- Piperidinyl side chain
- Thioridazine
- Piperazinyl side chain
- Trifluoperazine
- Prochlorperazine
- Perphenazine
- Fluphenazine
Whatever may be the side chains all these drugs show similar mechanism of action.
How phenothiazines act?
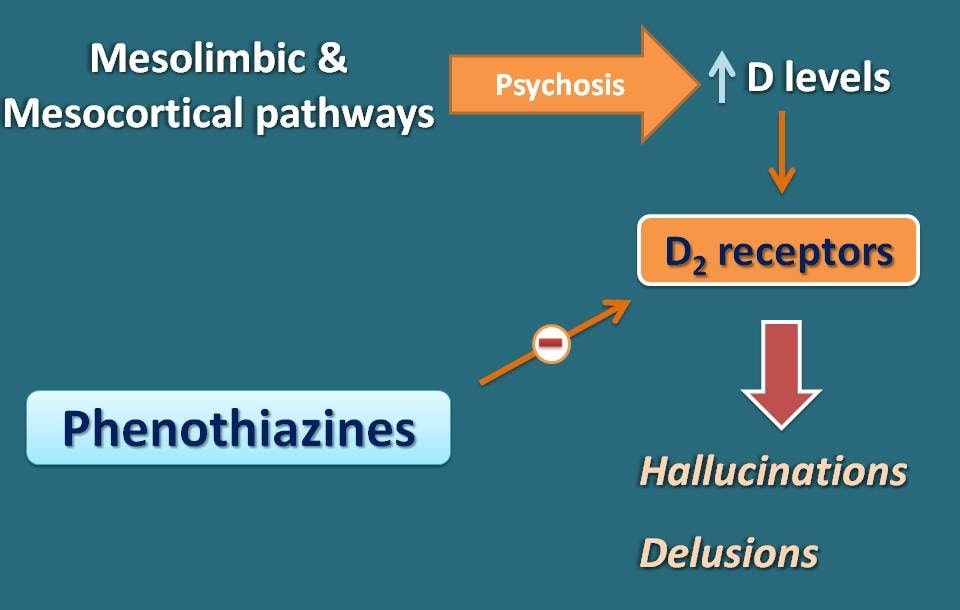
The mechanism of action of these drugs can’t be attributed to their action on a single receptor as they act on multiple types of receptors. Nevertheless, the antipsychotic action of these drugs is mainly attributed to their antagonism on dopamine receptors. These drugs act as antagonists on D2 receptors at mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways of dopamine where these receptors are excessively fired to produce psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia.
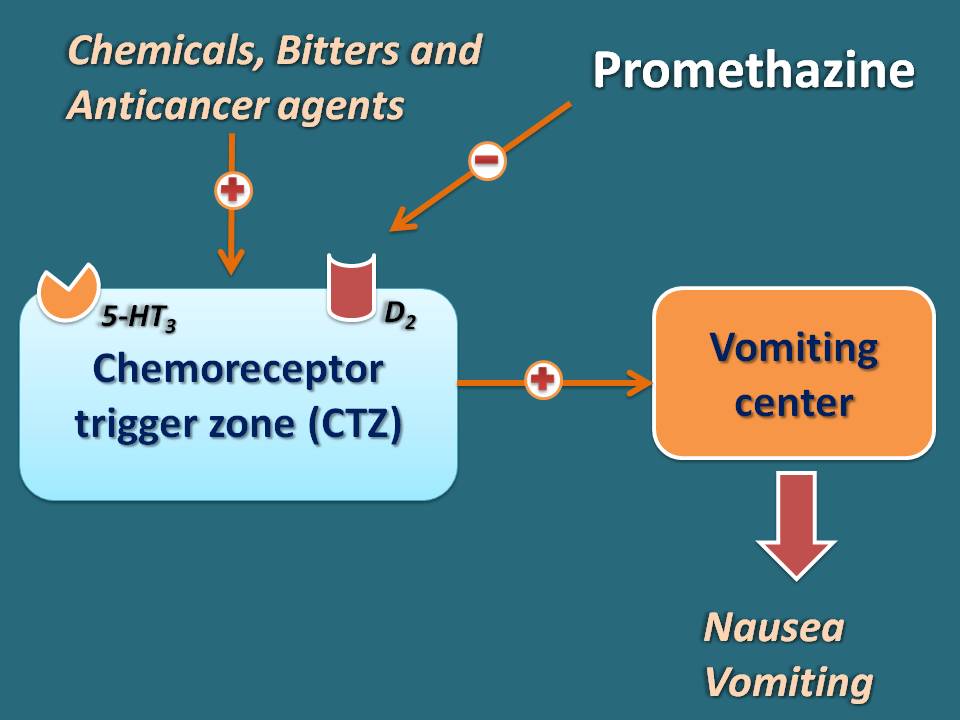
Another action of phenothiazines is their inhibitory effect on chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ). Of course, this action is again attributed to their antagonism on dopamine receptors. Normally, CTZ is stimulated by any toxic chemicals, bitter agents and many of the drugs like anticancer agents. All these chemicals act on dopamine receptors located on CTZ which stimulates nausea and vomiting. So, phenothiazines can prevent these stimuli by blocking dopamine receptors hence used as antiemetics.
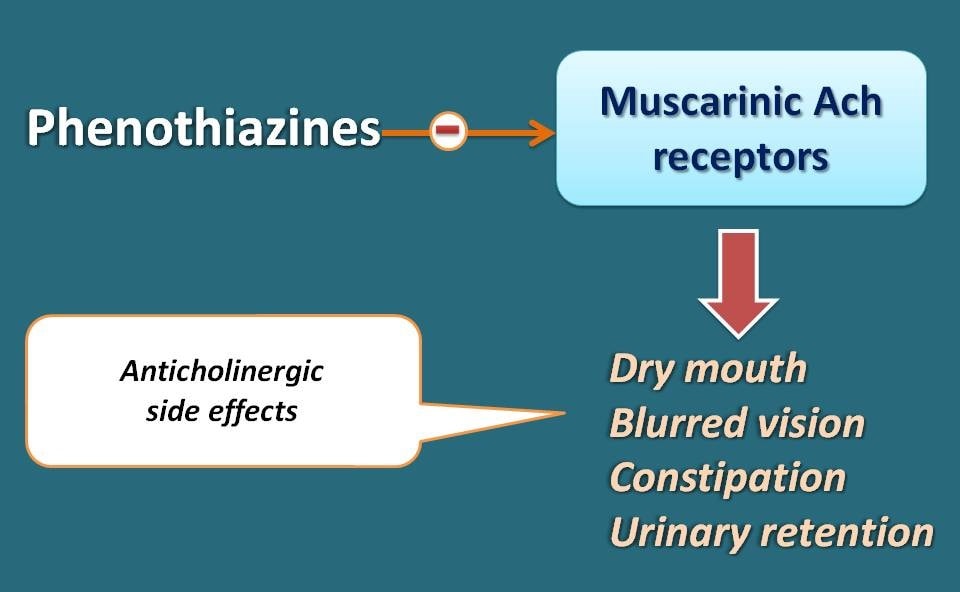
Phenothiazines also act as antagonists on muscarinic acetylcholine receptors producing anticholinergic actions. Most of the times, these actions such as constipation, dry mouth, blurred vision and urinary retention are observed as side effects with these drugs.
Finally, these drugs also act as antagonists on 5-HT receptors which may be responsible for their action on increase in body weight.

Side effects of phenothiazines
Phenothiazines can produce a range of side effects again attributd their action on multiple receptors. So, let’s see one by one here.
Extrapyramidal side effects
Being first generation antipsychotics, these drugs have more risk for producing extrapyramidal side effects compared with atypical antipsychotics. Of these acute dystonias, tardive dyskinesia and akathesia are three important components.
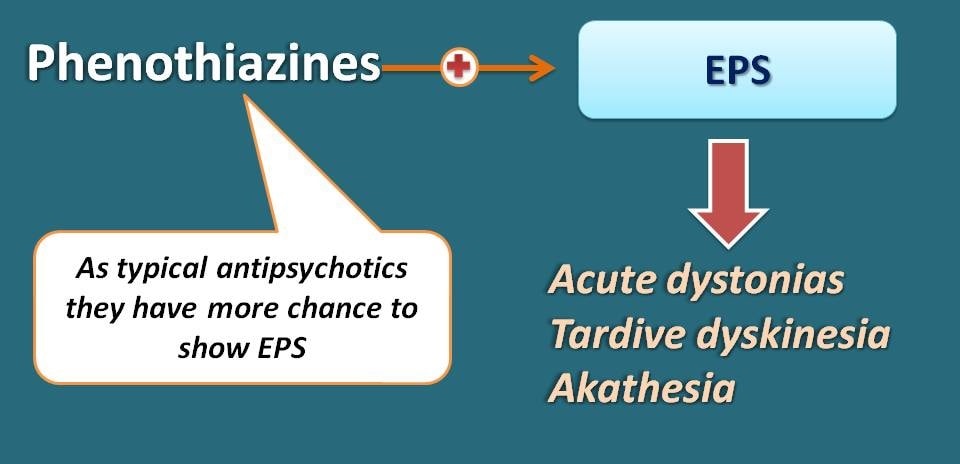
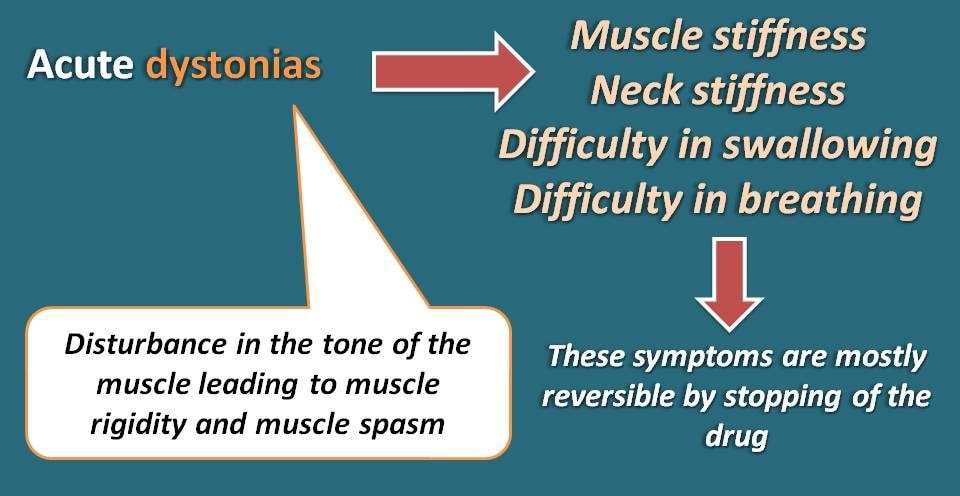
What are these acute dystonias?
As the name indicates, these symptoms are acute and are shortly developed after the drug usage. The term “dystonia” indicates that disturbance in the tone of muscle. These mainly include muscle rigidity and muscle spasms which may cause muscle pain, muscle stiffness, neck stiffness, difficulty in swallowing and breathing.
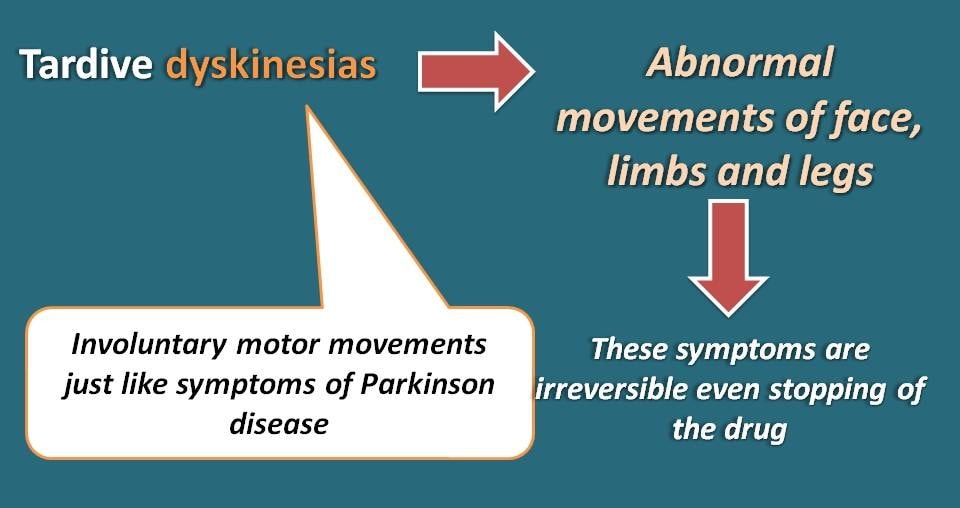
What about tardive dyskinesia then?
Again the term “tardive” indicates that symptoms are not observed immediately after the treatment but can be shown after several months of drug usage. The second term “dyskinesia” indicates disturbance in kinetics of muscle movement. In another words, these symptoms include involuntary movements of face, limbs and legs just resembling the symptoms of Parkinson disease.
Phenothaizines also cause restless, commonly known as akathesia, in the patients.

Other side effects
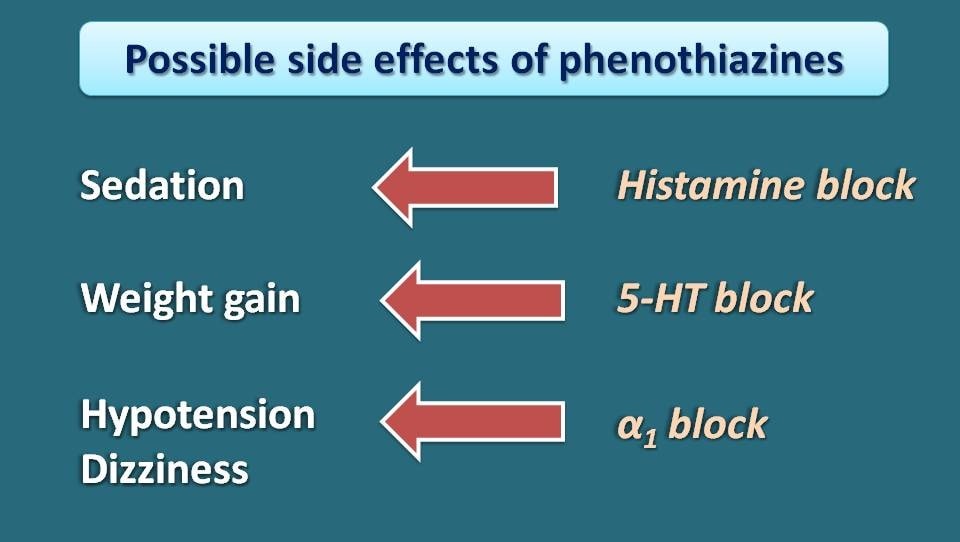
Apart from these EPS, phenothiazines also produce a list of side effects like hypotension, weight gain, constipation, blurred vision, dry mouth, urinary retention, sedation and confusion. Even though exact evidence is not clear all these side effects are attributed to action of phenothiazines on different receptors. For example, sedation is related to antagonism on histamine receptors while hypotension is due to α-receptor block.
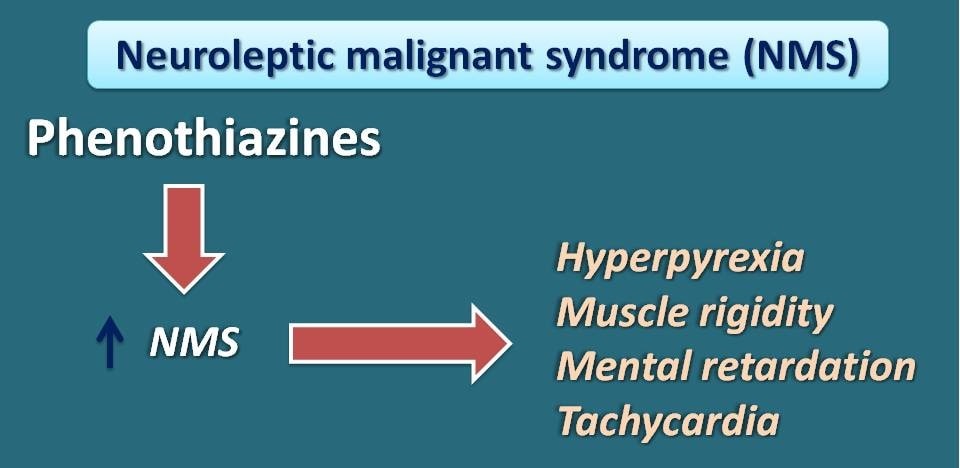
Neuroleptic malignant sysndrome
This is a severe side effect caused by many of the phenothiazines which results in abnormal raise in the body temperature of the patient. This hyperpyrexia is often associated with muscle weakness, tachycardia and mental retardation.
Clinical uses
With the introduction of atypical antipsychotics the clinical use of phenothiazines is somewhat declined. But still these drugs are approved for treating the psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia. Chlorpromazine, fluphenazine are good candidates for this usage.These drugs mainy act on positive symptoms of schizophrenia but less effective against negative symptoms such as social withdrawal in patients. Promethazine is another phenothiazine used as antiemetic.
