21 categories of drugs with multiple suffixes
by egpat 18-07-2017
In the previous article, we have discussed 40 categories of drugs with unique suffix. All these drugs can be identified by their suffix each representing their class. For example, drugs classified as ACE inhibitors always end with suffix “-pril” and converse is also true. That is, all the drugs ending with suffix “-pril” are ACE inhibitors.
But we can find few category of drugs with multiple suffixes or even few drugs in the category may have different suffix. For example, all the drugs ending with suffix “-azepam” are benzodiazepines but the converse is not true i.e. all benzodiazepines may not end with suffix “-azepam”. Drugs like alprazolam, triazolam and midazolam have a common suffix “-zolam” still they are benzodiazepines.
All the drugs ending with “-azepam” are benzodiazepines but all benzodiazepines may not end with “azepam”.
❞In this article, we will present category of drugs with multiple suffixes and how they are derived.
This time let’s start our discussion with categories arranged in alphabetical order.
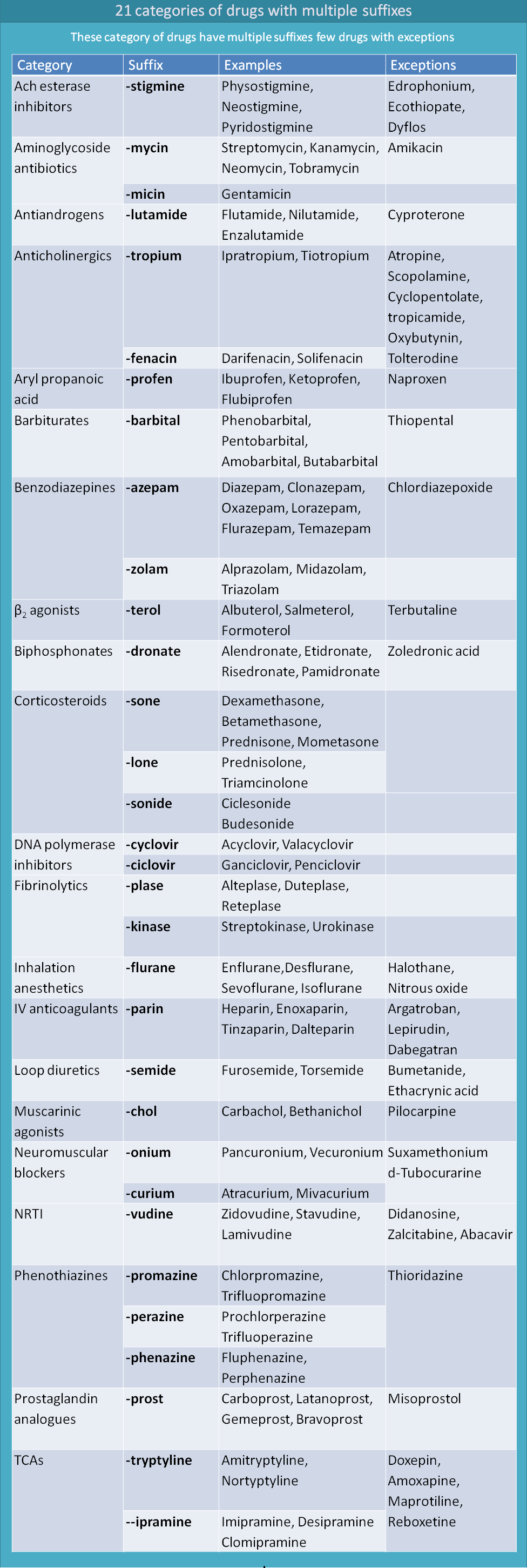
ACh esterase inhibitors
Ach esterase is one of the hydrolysing enzyme present at synaptic cleft of cholinergic neurons that metabolises the released acetylcholine rapidly. So, if this enzyme is inhibited, Ach levels can be increased leading to enhanced cholinergic transmission. Ach esterase inhibitors are of three types based on duration of action such as short acting, medium acting and long acting. Among these medium acting AChE inhibitors end with suffix “-stigmine”.
The story behind the suffix of AChE inhibitors comes from name of the natural product. Physostigmine is a natural alkaloid and all synthetic alkaloids derived then are named with suffix “-stigmine”.
Rivastigmine is a centrally acting AChE inhibitor that increases Ach levels within the CNS and hence indicated in AD.
Examples:
- Physostigmine
- Neostigmine
- Pyridostigmine
- Rivastigmine
Exception:
- Edrophonium
- Ecothiopate
- Dyflos
These drugs even belong to AChE inhibitors still doesn’t end with suffix “-stigmine”.
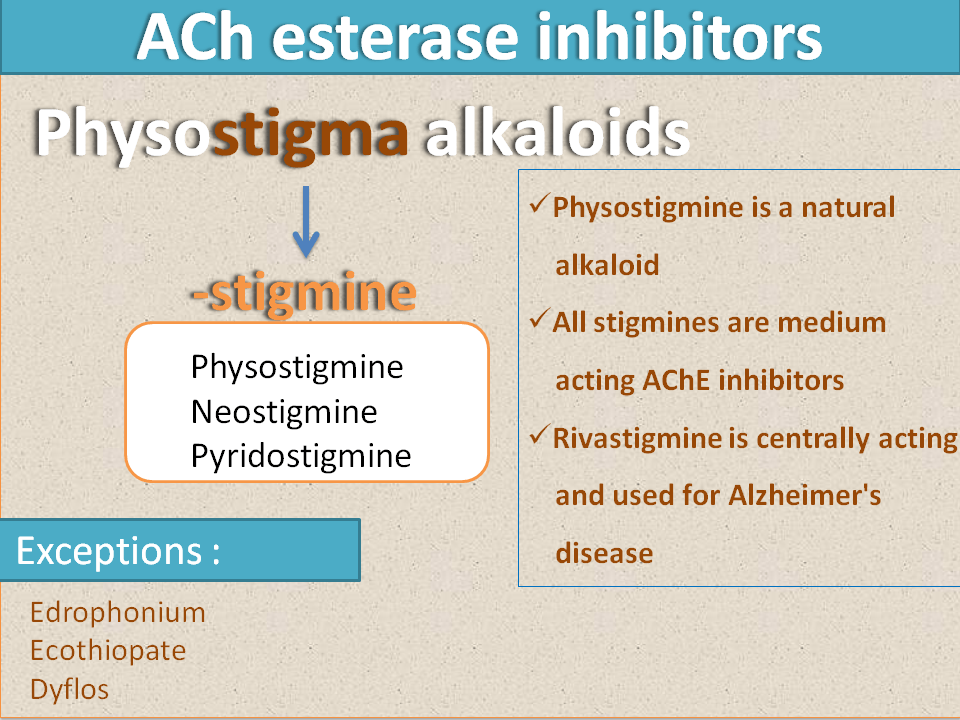
Aminoglycoside antibiotics
One of the oldest and well familiar group of antibiotics are aminoglycosides. These drugs act at protein synthesis of bacteria and prevent the reading of code in mRNA. They disrupt codon-anticodon pairing thereby inhibit protein sysnthesis in bacteria.
They end with suffix either “-mycin” or “-micin”. The difference in this suffix is due to their source from which they are derived. Those obtained from streptomyces species are named with suffix “-mycin” where “myc” indicates strptomyces. Similarly, Those obtained form micromonospora species are named as “-micin”
Examples:
- “-mycin”
- Streptomycin
- Kanamycin
- Neomycin
- Tobramycin
- “-micin”
- Gentamicin
These drugs should not be confused with macrolides like erythromycin which end with “-thromycin”.
Exceptions:
- Amikacin
Antiandrogens
Antiandrogens can be identified by suffix “-nilutamide”. These drugs antagonise the action of androgens and mainly used in the chemotherapy of prostate cancer.
Examples:
- Flutamide
- Nilutamide
- Enzalutamide
Exception:
- Cyproterone
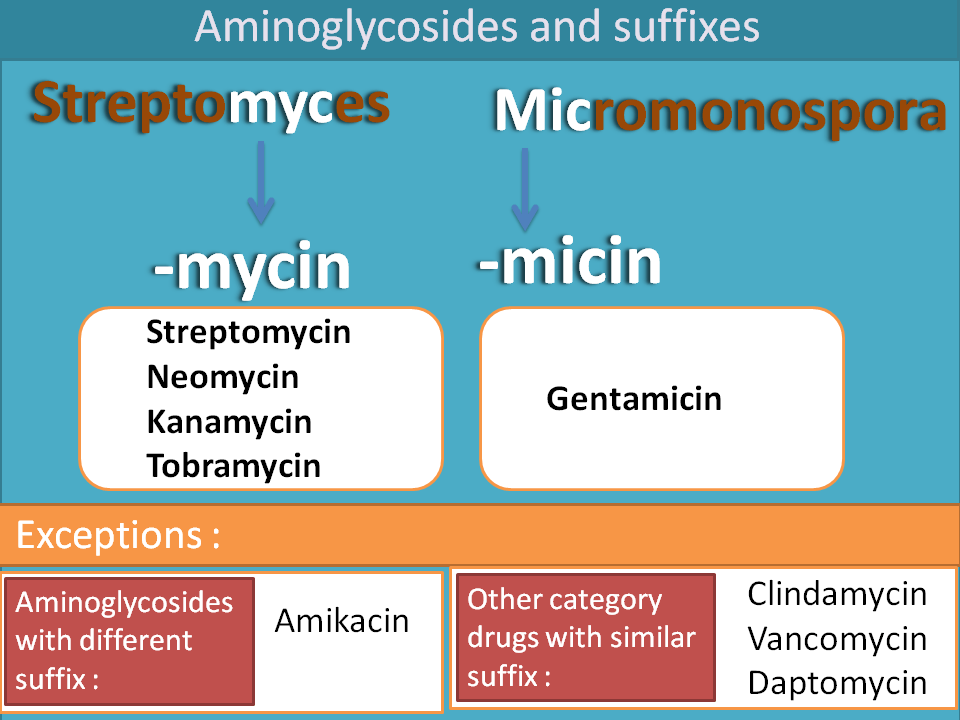
Anticholinergics
We have a wide variety of anticholinergics each acting on specific organ. For example, Ipratropium and tiotropium act on bronchioles leading to bronchodilatation. This doesn’t mean that they have no action on other organs, but they are intended for acting on the specific organ. These two drugs are synthetic analogues of tropane alklaoids, hence suffix “-trop” and again they have quaternary ammonium group , this time represented by suffix “-ium”.
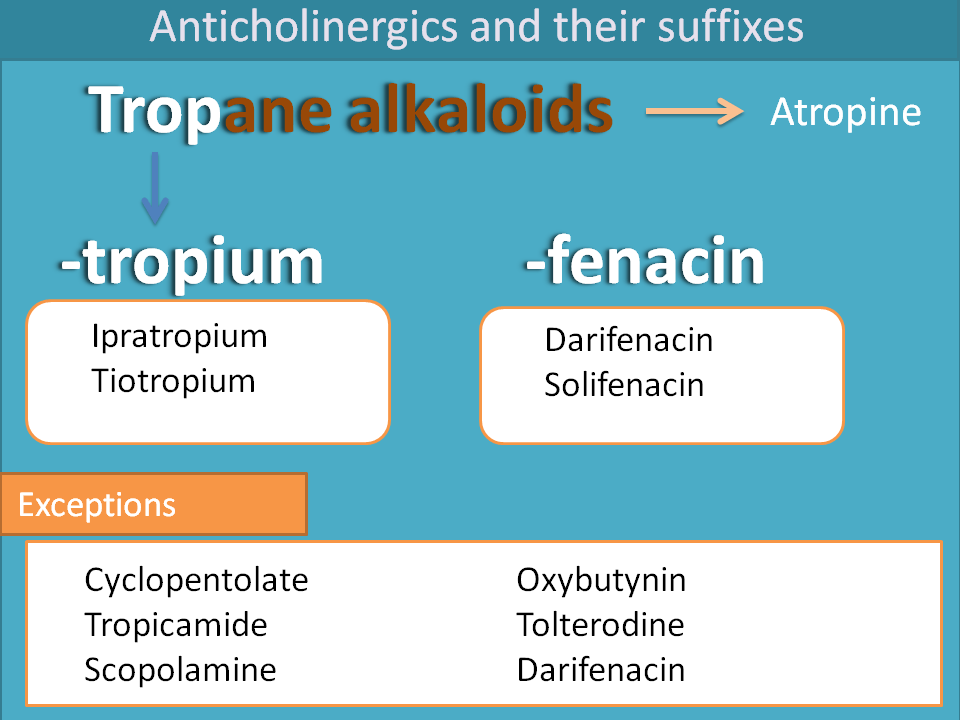
Similarly,darifenacin and solifenacin act on bladder as relaxants
Aryl propanoic acid
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents include a lot of chemical categories of which aryl propanoic acid derivatives are well familiar. These drugs inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme thereby inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, the later responsible for induction of pain, fever and inflammation. These drugs end with suffix “-profen” indicating that they are propanoic acid derivatives.
Examples:
- Ibuprofen
- Ketoprofen
- Flubiprofen
Exception:
- Naproxen
You can observe naproxen also includes “-pro-” within the name indicating its category.
Barbiturates
Barbiturates are oldest category of drugs that previously used as sedatives and anxioytics but due to their side effects they are mainly confined as anticonvulsants. All these end with “-barbital”
Examples:
- Phenobarbital
- Pentobarbital
- Amobarbital
- Butabarbital
Exception:
- Thiopental
Thiopental is an exception which is an ultra-fast acting barbiturate mainly used as IV anaesthetic.
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines belongs to the category of sedatives and anxiolytics that can decrease anxiety,aggressiveness and induce sleep. All these drugs end with suffix “-pam”. The suffix was given because all these drugs act as Positive Allosteric Modulators on GABAA receptors.
“Benzodiazepines act as Positive Allosteric Modulators on GABAA receptors hence suffixed as -pam”.
These drugs chemically derived from benzodiazepine ring hence suffix “-aze”. So, the suffix is obtained as Benzodiazepine + pam = “-azepam”
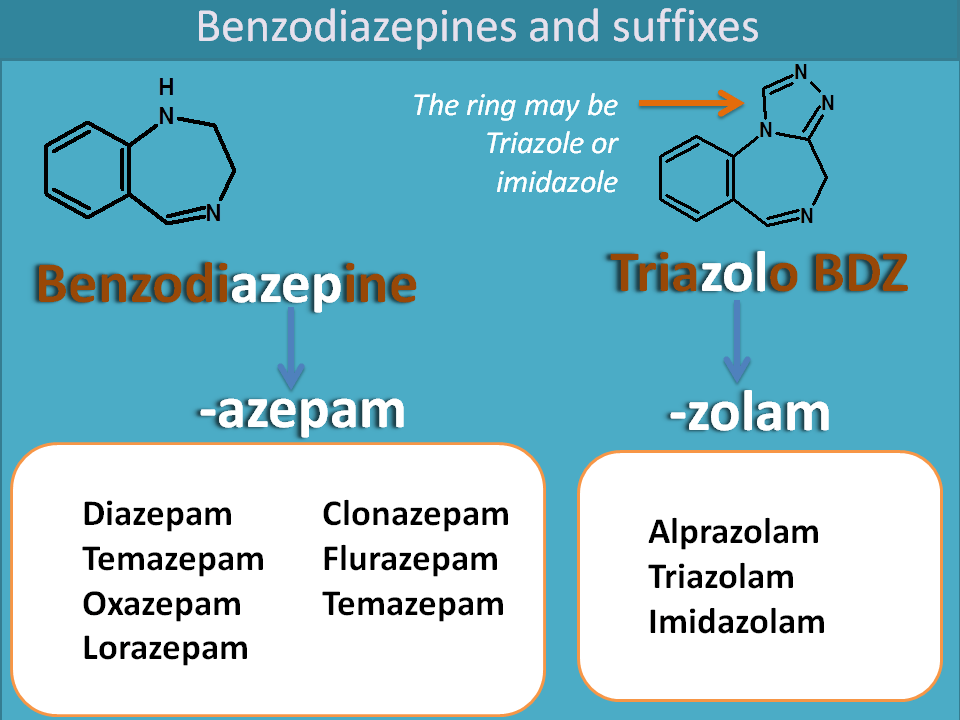
Examples:
- Diazepam
- Clonazepam
- Temazepam
- Flurazepam
- Lorazepam
- Oxazepma
- Quazepam
Another suffix we can observe in this category is “-zolam”. These are the drugs having fused benzodiazepine ring system such as triazolobenzodiazepine in alprazolam,triazolam and imidazolobenzodiazepine in midazolam.
- Alprazolam
- Triazolam
- Midazolam
Exception:
- Chlordiazpoxide
Chlordiazepoxide is the first drug that developed with absence of keto group at 2nd position.
Actually it is converted into active metabolites demoxepam and then oxazepam which have similar structure with all other pam drugs.
Beta 2 agonists
β2 receptors are mainly found on various smooth muscles including bronchial smooth muscle, GI smooth muscle, bladder, uterine and vascular smooth muscle. When they are activated they increase cAMP levels and produce relaxation. β2 agonists were developed to specifically act on bronchial smooth muscle as bronchodilators indicated in asthma. We can observe these drugs having common suffix “-terol”.
Examples
- Albuterol
- Salmeterol
- Formoterol
Albuterol is also called as salbutamol.
Exception:
Terbutaline is a short acting bronchodilator but it doesn’t has suffix “-terol”.
Biphosphonates
Biphosphonates are the category of drugs that inhibit bone resorption and even assist bone remodelling. Hence these drugs are used in osteoporosis and end with suffix “-dronate”
Examples:
- Alendronate
- Etidronate
- Risedronate
- Pamidronate
Exception:
- Zoledronic acid
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are the hormonal agents well known in the medical world. The natural corticosteroids are cortisone and hydrocortisone. These two drugs have steroidal ring and show both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid activity. Synthetic steroids were developed by structural modification in order to increase glucocorticaoid acitivity and suppress the mineralocorticoid acitivity.
These drugs show three patterns in the suffix. Most of the drugs end with “-sone” or “-lone” while few other drugs end with “-sonide”.
Examples:
- -sone
- Prednisone
- Dexamethasone
- Betamethasone
- Mometasone
- Fluticasone
- -lone
- Prednisolone
- Methylprednisolone
- Triamcinolone
- -sonide
- Budesonide
- Ciclesonide
DNA polymerase inhibitors
These are the group of drugs highly active against herpes virus infections. These drugs inhibit DNA polymerase enzyme thereby inhibit viral DNA replication. These drugs show two types of suffixes. Few drugs like acyclovir, valacyclovir end with suffix “-cyclovir” whereas other drugs like ganciclovir and penciclovir end with suffix “-ciclovir”.
We can observe that both of the suffixes end with “-vir” indicating their broad category as antiviral.
- -cyclovir
- Acyclovir
- Valacyclovir
- -ciclovir
- Ganciclovir
- Penciclovir
- Famciclovir
- Valganciclovir
Exceptions
Foscarnet is a both DNA and RNA polymerase inhibitor used for herpes infections.
Fibrinolytics
Fibrinolytics are the tissue plasminogen activators that convert plasminogen to plasmin. The latter then breaks the fibrin mesh dissolving the clot. Therefore these drugs are enzyme preparation and hence end with “-ase”. Further, they can have two types of suffixes such as “-kinase ” and “-plase”.
Examples:
- -kinase
- Streptokinase
- Urokinase
- -plase
- Alteplase
- Duteplase
- Reteplase
Inhalation anesthetics
Most of the inhalation anaesthetics today are derivatives of fluorinated hydrocarbons. Hence their suffix is taken as “-flurane”.
Flu orinated + ane (hydrocarbons)=“-flurane”
Examples
- Isoflurane
- Enflurane
- Desflurane
- Sevoflurane
Exception
- Halothane
- Nitrous oxide
IV anticoagulants
Thrombin inhibitors such as heparin are mainly used as IV anticoagulants. These drugs inhibit the activated coagulation factors such as factor IIa and Xa thereby inhibit coagulation cascade. All these drugs end with suffix “-parin” derived from parent compound heparin.
Examples:
- Heparin
- Enoxaparin
- Tinzaparin
- Dalteparin
Exceptions:
- Argatroban
- Lepirudin
- Dabegatran
Loop diuretics
Loop diuretics are the drugs that act at ascending loop of henle and inhibit Na+/K+-ATPase pump inhibiting sodium reabsorption. In this way they increase sodium excretion along with other minerals like potassium, calcium, magnesium and chloride. Two of the drug in this category end with suffix “-semide”.
Examples:
- Furosemide
- Torsemide
Exception:
- Ethacrynic acid
- Bumetanide
Muscarinic agonists
We have only three drugs available in this category of which pilocarpine is a natural alkaloid. Other two drugs are structural modification of acetylcholine to increase stability and specificity on muscarinic receptors.
These include carbachol and bethanichol both ending with the suffix “-chol”. This suffix is derived from the name of Acetylcholine.
Examples;
- Carbachol
- Bethanichol
Exception:
- Pilocarpine
Neuromuscular blockers
This category of drugs acts by blocking the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nACh receptors) at skeletal muscle. These are of two types viz. depolarising and non-depolarising. d-Tubocurarine is a natural alkaloid that acts a non-depolarising neuromuscular blocker. In olden days it is applied to the edge of arrow for hunting of wild animals and when it pierces into the skin of animal it relaxes the skeletal muscle so that animal cannot run and escape.
Synthetic drugs developed afterwards and named as “-curonium”. This is partly taken from suffix of d-tubocurarine and partly from the functional group i.e. quaternary ammonium.
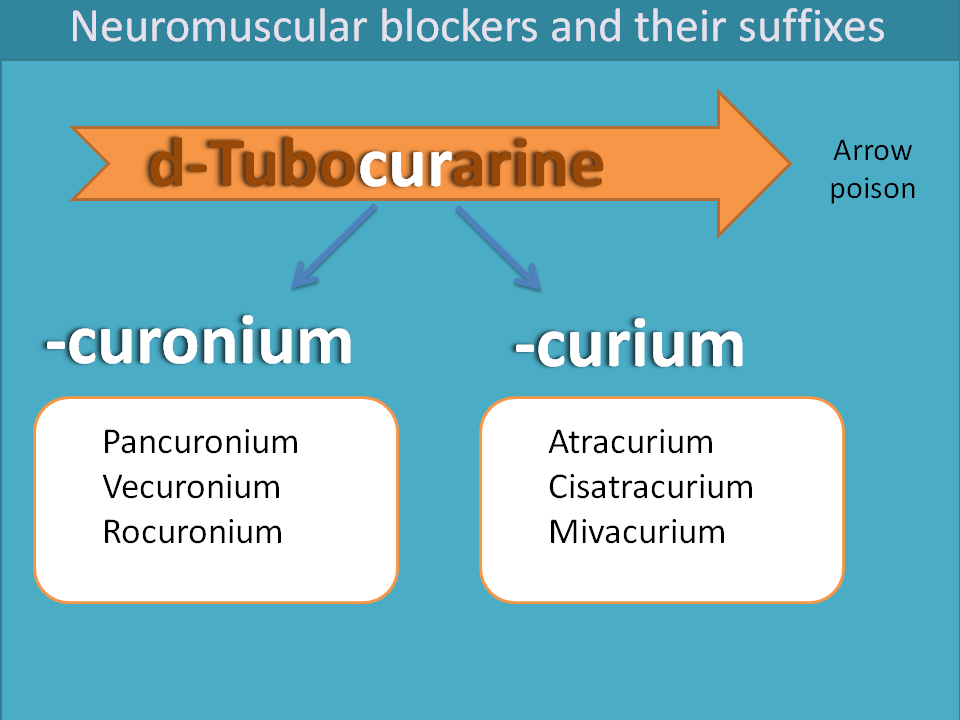
We can also find another set of neuromuscular blockers with suffix “-curium”. These drugs are very short acting producing the muscle paralysis for short surgical procedures.
Examples:
- -curonium
- Pancuronium
- Vecuronium
- Rocuronium
- -curium
- Atracurium
- Cisatracurium
- Mivacurium
Exception:
- Suxamethonium
- D-Tubocurarine
- Gallamine
NRTI
Reverse transcriptase is the key enzyme in retrovirus that produces viral DNA from viral RNA. This enzyme can be inhibited by a class of drugs just resembling a nucleoside are called as Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI). These drugs end with suffix “-vudine”.
Examples
- Zidovudine
- Lamivudine
- Stavudine
Exceptions:
- Didanosine
- Zalcitabine
- Abacavir
Phenothiazines
Typical antipsychotics are old generation drugs which are effective in the treatment of schizophrenia. Among these phenothiazines play vital role by blocking dopaminergic receptors in mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways. These drugs can have two types of suffix based on the side chain present on the phenothiazine ring. Those drugs having propyl amino side chain are named with suffix “-promazine” and those with piperazine side chain are named either “-phenazine” or “-promazine”.
- “-promazine”
- Chlorpromazine
- Trifluopromazine
- “-perazine”
- Prochlorperazine
- Trifluoperazine
- “-phenazine”
- Perphenazine
- Fluphenazine
Exception:
- Thioridazine
Prostaglandin analogues
Prostaglandins are the local mediators playing various roles like vasodilatation, platelet aggregation, uterine contraction etc. So prostaglandin analogues can be used in various contexts but all these drugs have same suffix “-prost”.
TCAs
Tricyclcic antidepressants, as name itself indicating, have three rings in their structure. These drug inhibit uptake 1 process at adrenergic and seroninergic neurons thereby increase noradrenaline and 5-HT levels. Again these drugs show two types of suffixes viz. “-triptyline” and “-ipramine”.
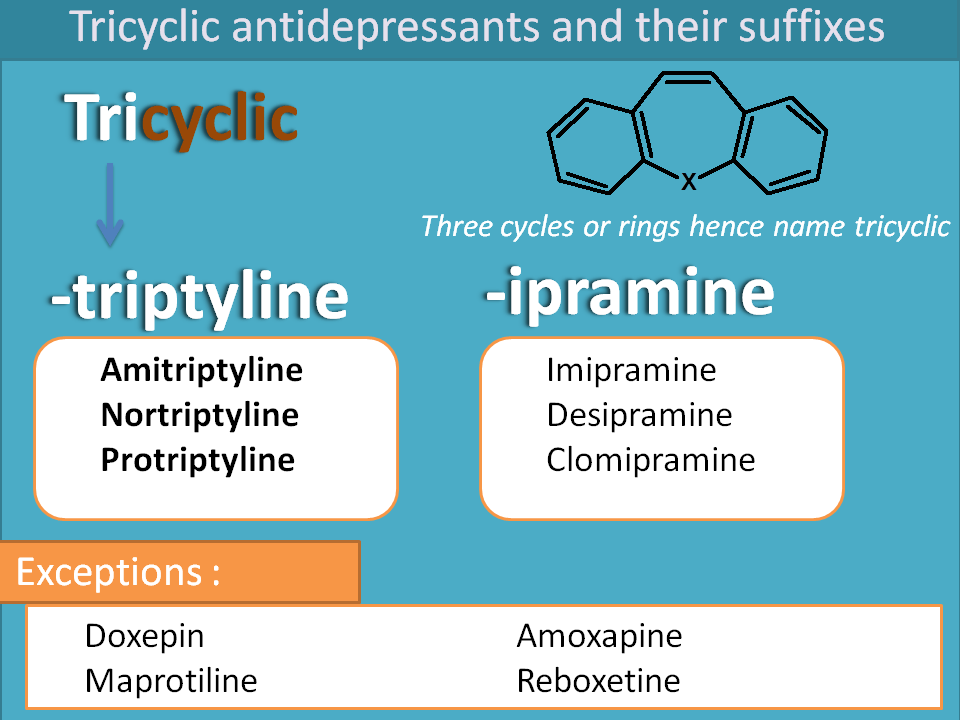
Examples:
- -triptyline
- Amitriptyline
- Nortriptyline
- Protriptyline
- -ipramine
- Imipramine
- Clomipramine
- Desipramine
- Trimipramine
Exception:
- Doxepin
- Maprotiline
- Reboxetine
Maprotyline is a tetracylcic antidepressant.
That's the story of 21 categories of drugs with multiple suffixes or even with exceptions. As clinical research is going on new drugs may add to this list.
Find here a video on all these 21 categories of drugs with multiple suffixes.
Here is the summary of all drugs we have discussed in tabular format.
Hope you have enjoyed reading this article !