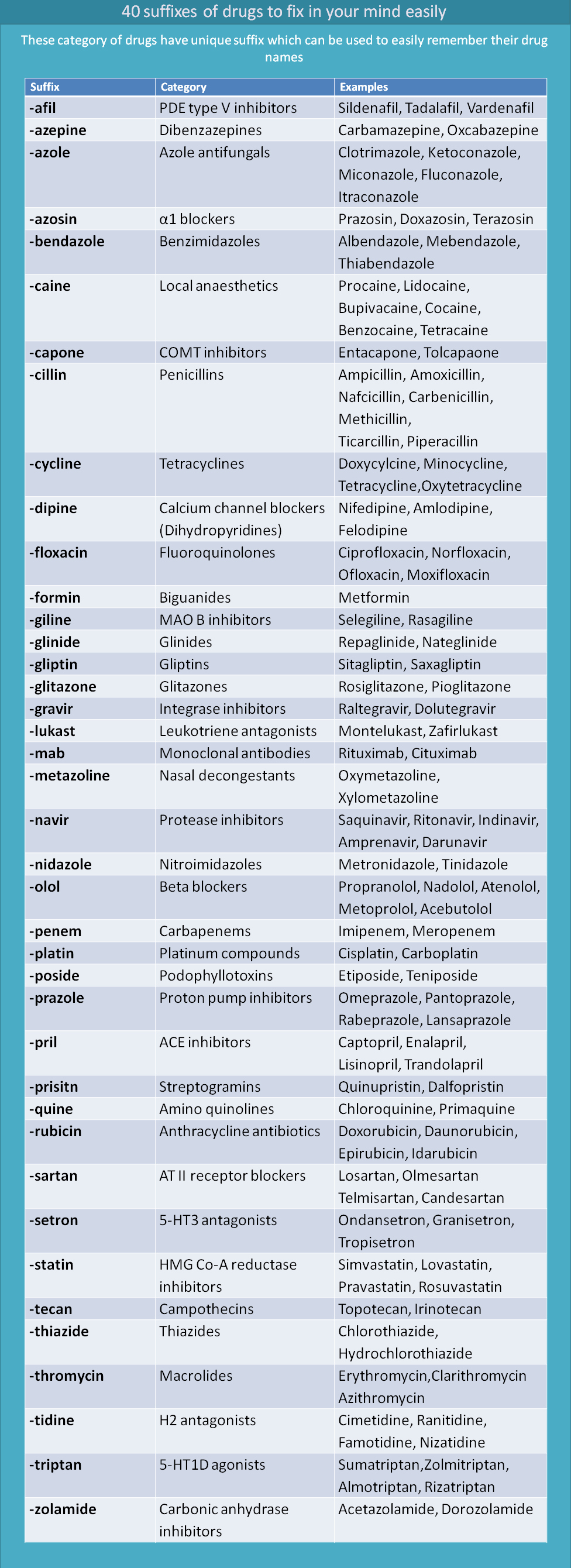
40 suffixes of drug names to fix in your mind easily
by egpat 17-08-2017
Remembering drug names is a difficult task with the ever-growing list of drugs in pharmacology. Drugs are first categorized into a particular category, either based on their target and mechanism or based on their chemical nature. For example, beta blockers are a class of drugs that block beta adrenergic receptors, whereas benzodiazepines are a class of anxiolytics named according to their chemical structure. Whatever the reason behind the naming of the drugs, we can observe some logic and rhythm in a few categories of drug names. In this article, we will present 40 categories of drugs, each with a unique suffix that is easy to identify.
We have not included here a few of the categories that have multiple suffixes. For example, benzodiazepines can have the suffix "-azepam" or "-zolam." We will present these drugs in our next article.
So let's start our discussion with suffixes arranged in alphabetical order.
PDE type V inhibitors: "-afil"
Phosphodiesterae (PDE) is a metabolic enzyme for cAMP and cGMP which are the mediators that produce vasodilatation and smooth muscle relaxation. So, PDE inhibitors block this metabolism raising cAMP/cGMP levels. PDE type V is present in erectile tissue and when it is inhibited vasodilatation and subsequent erection is observed. Hence PDE type V inhibitors are used for erectile dysfunction. You can identify their drug names by suffix “-afil”.
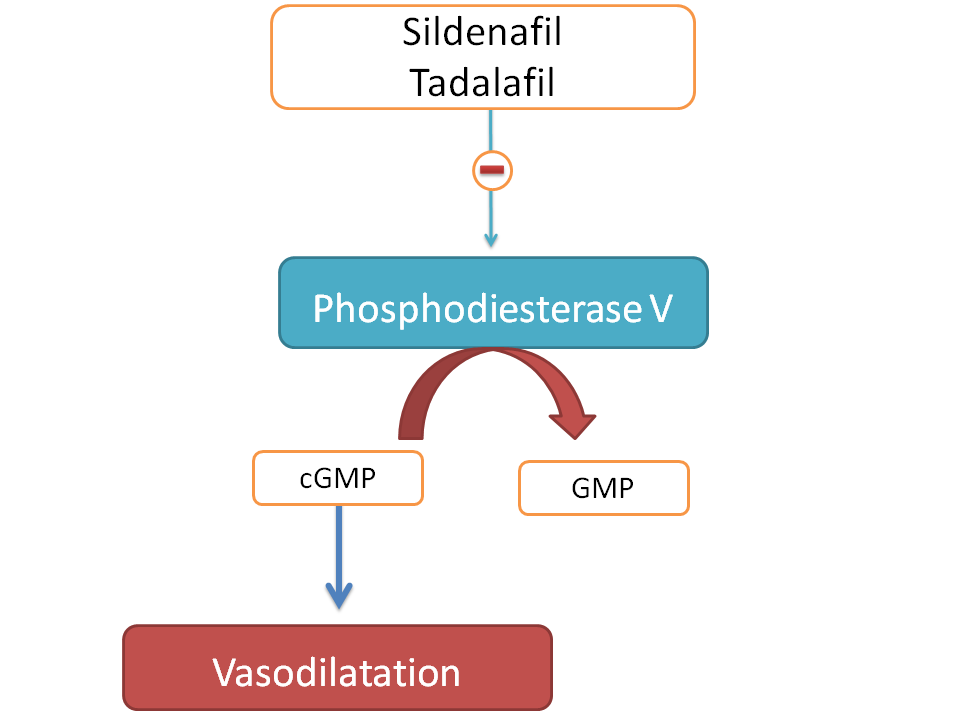
Examples:
- Sildenafil
- Tadalafil
- Vardenafil
Dibenzazepines : "-azepine"
Carbamazepine is an anticonvulsant that inhibits voltage gated sodium channels and indicated in tonic-clonic and focal seizures. Chemically it belongs to dibenzazepine where two benzene rings are fused with seven membered nitrogen containing (hence azepine) ring.
Examples:
- Carbamazepine
- Oxacarbazepine
It should not be confused with benzodiazepines which have only one benzene ring but two nitrogens. The drug names of benzodiazepines will have different suffix “-azepam”.
Azole antifungals : "-azole"
One of the widely prescribed antifungal agents are azole antifungals. These drugs have either imidazole or triazole ring in their structure hence suffix “-azole ” is used in their drug names.
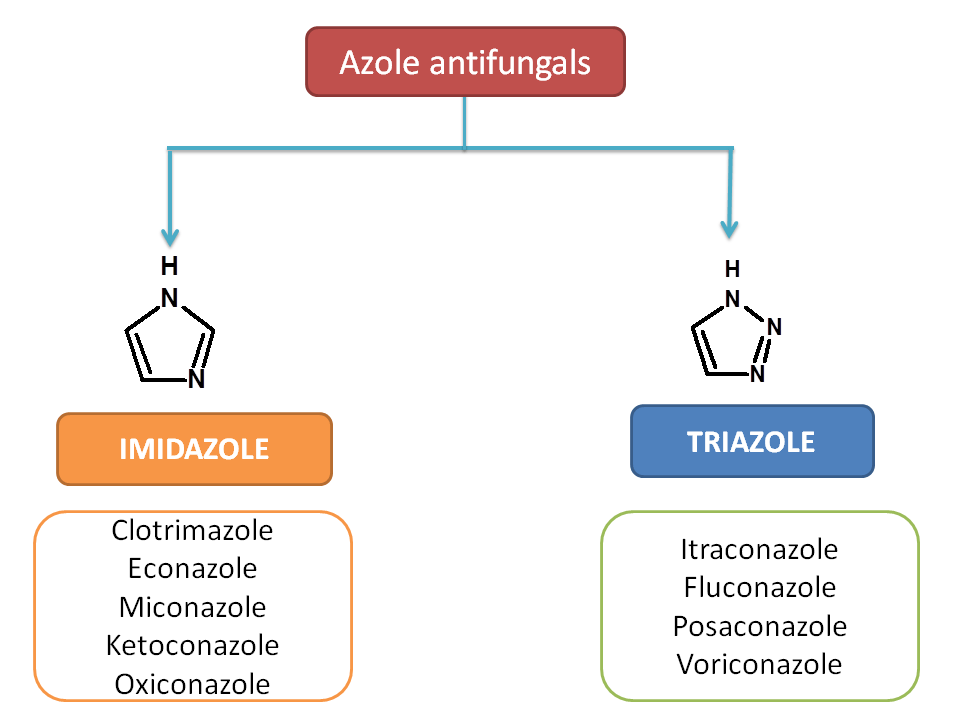
Examples:
- Imidazole antifungals
- Clotrimazole
- Ketoconazole
- Econazole
- Miconazole
- Oxiconazole
- Terconazole
- Tioconazole
- Triazole antifungals
- Fluconazole
- Itraconazole
- Posaconazole
- Voriconazole
α1 blockers : "-azosin"
α1 blockers directly act on vascular smooth muscle and inhibit α1 adrenergic receptors leading to vasodilatation. These drugs can be identified by suffix “-azosin”.
Examples:
- Prazosin
- Doxazosin
- Terazosin
However, few alpha blockers that show little activity in the bladder have a similar suffix as -osin. They include
- Tamsulosin
- Alfuzosin
- Silodosin
Benzimidazoles : "-bendazole"
Benzimidazoles play a vital role in controlling helmenthis infections particularly . These drugs target the microtubule formation in the parasites. Currently, this group has three drugs all ending with “-bendazole”.
Examples:
- Albendazole
- Mebendazole
- Thiabendazole
Local anaesthetics : "-caine"
Local anaesthetics act by blocking voltage gated sodium channels and inhibit local neurotransmission. Cocaine is a natural alkaloid that acts as local anaesthetic but at the same time it is a CNS stimulant producing euphoria and leads to addiction. Hence synthetic drugs were prepare which acts like cocaine and named with suffix “-caine” similar to cocaine.
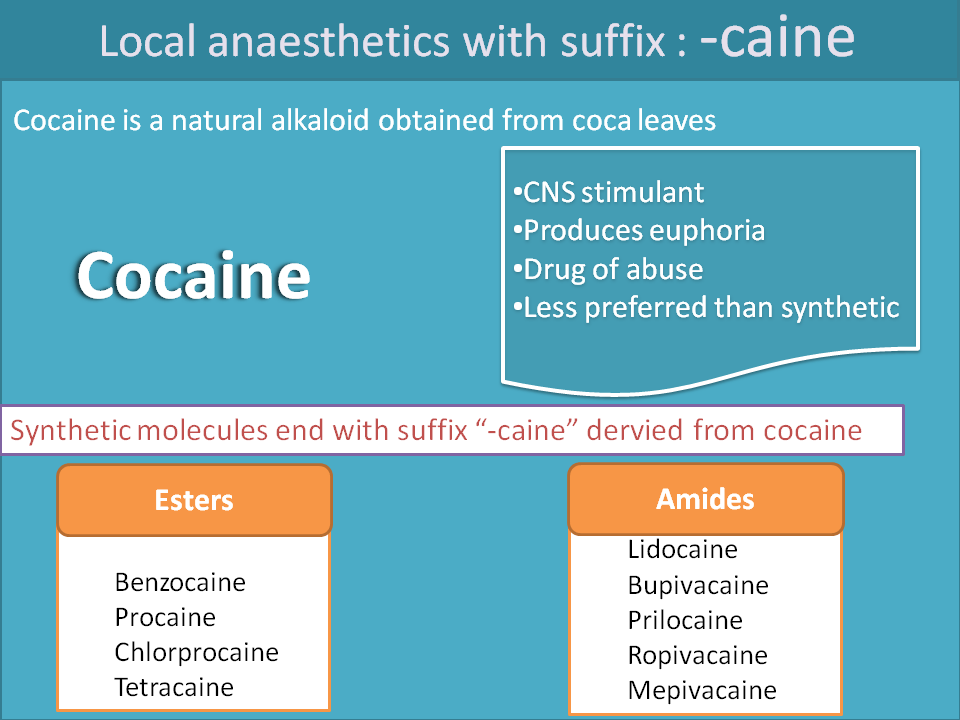
Examples:
- Ester derivatives
- Cocaine
- Benzocaine
- Procaine
- Chlorprocaine
- Tetracaine
- Amide derivatives
- Lidocaine
- Bupivacaine
- Prilocaine
- Ropivacaine
- Mepivacaine
COMT inhibitors
Catechol-O-methyl transferase is one of the enzyme metabolising catechol amines like adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine. It even responsible for metabolism of external catechol amines like levodopa. Hence COMT inhibitors can be used to inhibit the peripheral metabolism of levodopa increasing their levels within the CNS.
Examples:
- Entacapone
- Tolcapone
Penicillins : "-cillin"
A well known group of antibiotics that play a central role in chemotherapy are penicillins. Penicliin G and Penicillin V are natural penicillins. These drugs are structurally modified to improve stability, decrease resistance and even extend their spectrum to produce new generation penicillins. All these drug names end with “-cillin” taken from natural penicillins.

Tetracyclines : "-cycline"
This is another group of antibiotics that inhibit ptoteins synthesis in bacteria by inhibitin attachment of tRNA to the A site on 50S ribosome. All these drugs can be easily identified by suffix “-cycline”.
Examples:
- Doxycylcine
- Minocycline
- Tetracycline
- Oxytetracycline
Dihydropyridines : "-dipine"
This is one group of calcium channel blockers that directly act on vascular smooth muscle and produce vasodilatation. These drugs are chemically derived from a ring dihydropyridine from which suffix was taken.
Dihydropyridine=-dipine
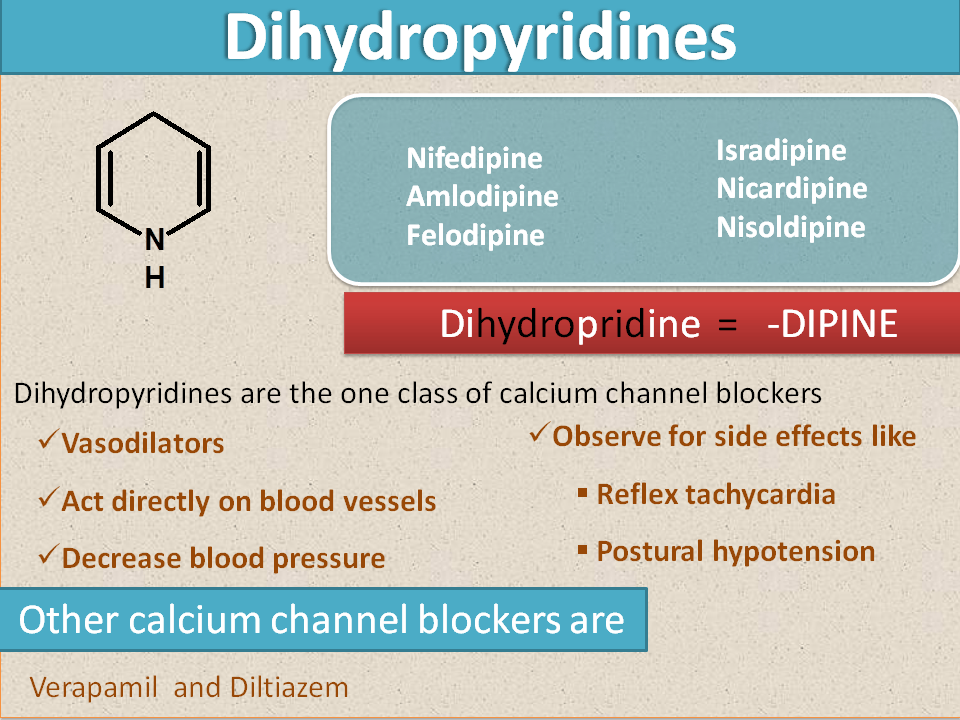
- Nifedipine
- Amlodipine
- Felodipine
- Isradipine
- Nicardipine
- Nisoldipine
Fluoroquinilones : "-floxacin"
This is a unique group of antibiotics that inhibit topoisomerase (DNA gyrase) affecting the replication of DNA in bacteria. All generations of fluoroquinolone drug names end with “-floxacin”.
Examples:
- Ciprofloxacin
- Norfloxacin
- Ofloxacin
- Levofloxacin
- Moxifloxacin
Nalidixic acid is a first generation quinlone that also belongs to this categroy but structurally it doesn't has fluorine hence doesn't has suffix "-floxacin".
Biguanides : "-formin"
Biguanides are oral hypoglycaemic agents that not only decrease glucose levels but also produce weight loss hence preferred in diabetic patients with overweight. Only one drug available in the market with suffix “-formin”
MAO B inhibitors : "-giline"
MAO B inhibitors inhibit central metabolism of monoamines like dopamine and thereby increase their levels within the CNS. These drugs are indicated in Parkinson disease (PD). They end with suffix “-giline”.
- Selegiline
- Rasagiline
Glinides : "-glinide"
Glinides are the structurally not similar to sulfonyl ureas but act like sulfony ureas inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium channels and there by releasing insulin.
- Repaglinide
- Nateglinide
Gliptins : "-gliptin"
Incretin hormones such as glucagon like insulinotropic peptide-1 (GLP-1) are released from gastro intestinal (GI) tract in response to a meal and act like insulin controlling glucose levels. These drugs are inactivated by dipeptidyl peptidae IV (DPP-IV) enzyme. Gliptins are class of drugs that inhibit DPP IV thereby increase GLP-1 and control glucose levels.
- Sitagliptin
- Saxagliptin
Glitazones : "-glitazone"
Glitazones are another category of antidiabetic agents that act on nuclear receptors such as PPARγ and enhance glucose uptake from blood into liver and muscle.
- Rosiglitazone
- Pioglitazone
Integrase inhibitors : "-gravir"
Now let’s see another category proved beneficial in the treatment of HIV. Integrase is one of the enzyme in HIV that merges its viral DNA with host DNA forming a mixed type of DNA that can undergo transcription generating more viral proteins. So, it is a novel target to control propagation of HIV in the host.
We can observe suffix taken from two words i.e . integrase and antiviral =-gravir
- Raltegravir
- Dolutegravir
Leukotriene antagonists : "-lukast"
Leukotriene is involved in producing allergic response and bronchospasm. Their antagonists are mainly used in allergic conditions like rhinitis and asthma.
- Montelukast
- Zafirlukast
Monoclonal antibodies : "-mab"
Drugs of this class have suffix taken from their class name “-mab”. These drugs can suppress the cancerous cells by targeting a specific growth factor expressed on the cells. They can also act as biological modifiers that neutralize the specific antigens on T cell surface decreasing the host immunity. They are required in special conditions like organ transplantation where host immunity should be suppressed to prevent rejection of organ.
- Rituximab
- Cituximab
- Trastuzumab
- Bivacizumab
- Omalizumab
- Abciximab
Nasal decongestants : "-metazoline"
Drugs acting as agonist on α1 receptors produce nasal vasoconstriction and hence used as nasal decongestants.
- Oxymetazoline
- Xylometazoline
Protease inhibitors : "-navir"
We can easily identify antiviral agents by suffix “-vir” but all these drugs does not act equally and even doesn’t indicated equally. One class of drugs ending with “-navir” inhibit protease enzyme present in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and used as anit-HIV agents.
- Saquinavir
- Ritonavir
- Indinavir
- Amprenavir
- Darunavir
Nitroimidazoles : "-nidazole"
Again these should not be confused with azole antifungals or benzimidazoles. These are antiameobic agents that produce oxidative damage to the parasite’s DNA. These drug names have suffix “-nidazole”.
- Metronidazole
- Tinidazole
Beta blockers : "-olol"
All beta blockers both selective and non-selective can be easily identified by suffix “-olol”.
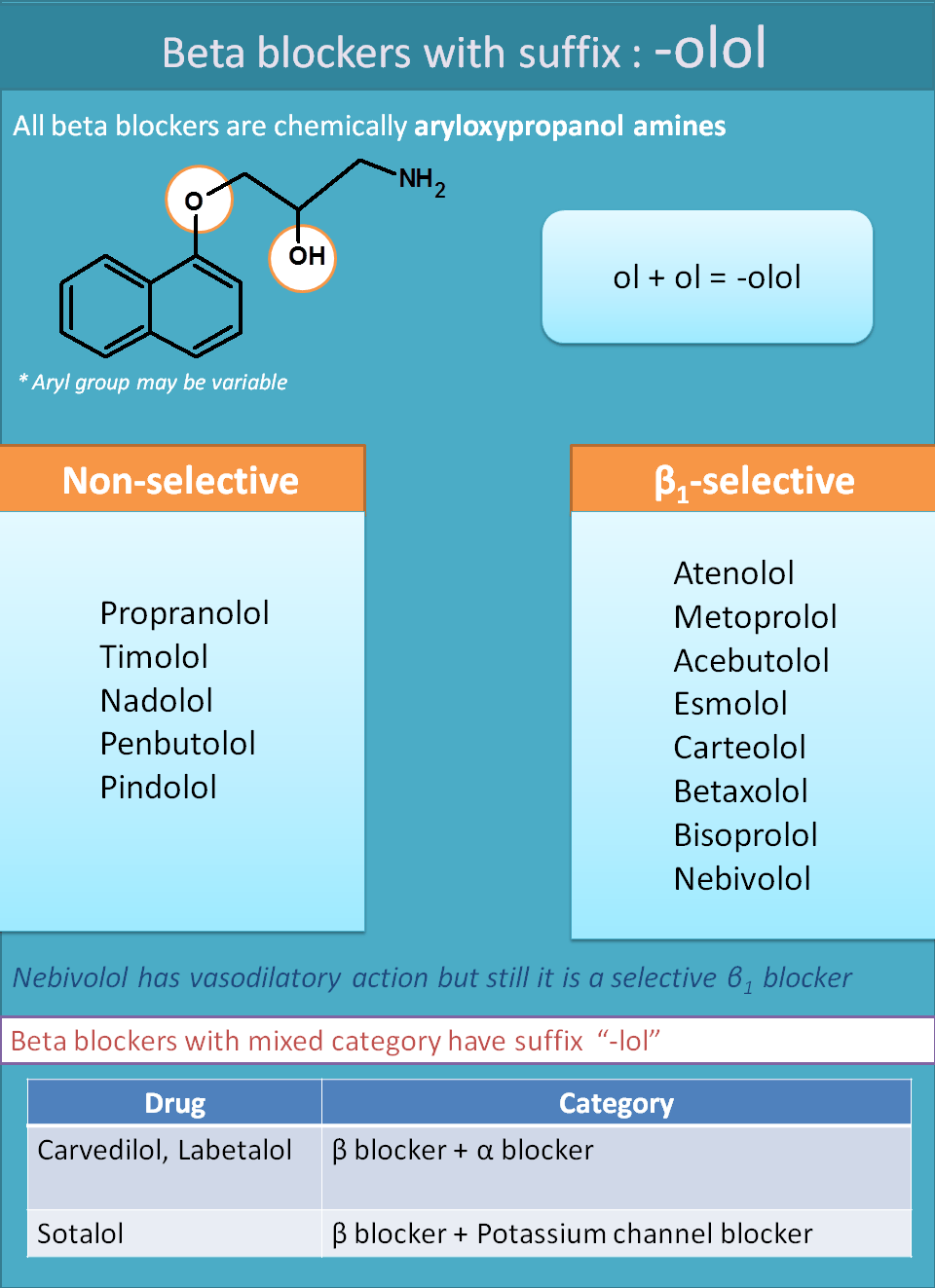
- Non-Selective beta blockers
- Propranolol
- Nadolol
- Timolol
- Selective β1 blockers
- Atenolol
- Metoprolol
- Esmolol
- Acebutolol
You can easily identify the suffix “-olol” in all the above drugs. But still you can observe few beta blockers not ending with “-olol”. These drugs not only belong to beta blocker category but they are mixed categories.
These drugs show an additional activity along with beta blocking activity.
- Carvedilol
- Labetalol
- Sotalol
Carbapenems : "-penem"
This group is obtained by ring modification of penicillins by bringing sulfur out of the ring. These drugs end with suffix “-penem”.
- Imipenem
- Meropenem
Platinum compounds : "-platin"
Platinum comounds act as alkylating agents and form cross linkage between the strands of DNA. Their suffix “-platin” easily indicates their category.
- Cisplatin
- Carboplatin
Podophyllotoxins : "-iposide"
This is another category of anticancer agents coming from natural source i.e. podophyllum. These drugs inhibit topoisomerase II and end with suffix “-poside”.
- Etiposide
- Teniposide
Proton pump inhibitors : "-prazole"
Nowadays, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are the one of the widely prescribed drugs to prevent excess release of gastric acid by all types of stimuli. They have a prophylactic role when used with NSAIDs preventing ulcer formation. These drug names end with suffix “-prazole” which should not be confused with “-azoles”.
- Omeprazole
- Rabeprazole
- Pantoprazole
- Lansoprazole
- Esomeprazole
- Dexlansoprazole
ACE inhibitors : "-pril"
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors act on rennin-angiotensin system and inhibit the formation of AT II from AT I by ACE enzyme. All these drugs end with suffix “-pril”. These drugs include
- Captopril
- Lisinopril
- Enalapril
- Ramipril
- Trandopril
- Fosinopril
Streptogramins : "-pristin"
Streptogramins inhibit protein synthesis in bacteria. Two drugs in this category are used in combination both ending with “-pristin”.
- Quinupristin
- Dalfopristin
Amino quinolines : "-quine"
Qunine is a natural product that is used as antimalarial agent. Synthetic molecules like 4-aminoquinolines and 8-aminoquinolines are then derived. All these drugs have quinolie ring system and represented by common suffix “-quine”.
- Chloroquine
- Primaquine
Anthracycline antibiotics : "-rubicin"
Anthracycline antibiotics are a group of cytotoxic antibiotics that mainly act on DNA polymerase enzyme and inhibit DNA replication. These can be identified by suffix “-rubicin”.
- Doxorubicin
- Daunorubicin
- Epirubicin
- Idarubicin
Angiotensin II receptor blockers : "-sartan"
Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) block the action of angiotensin II (AT II) on its receptors and thereby inhibit all its actions mediated particularly vasoconstriction. This category of drugs have suffix “-sartan”.
- Losartan
- Olmesartan
- Candesartan
- Irbesartan
- Valsartan
- Telmisartan,
- Eprosartan
- Azilsartan
5-HT3 antagonists : "-setron"
Emesis is a reflex action produced by stimulation chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) within the CNS. Area postrema is a region within the CTZ expressed with 5-HT3 receptors which stimulate vomiting reflex. Drugs such as “setrons” can block these receptors acting as antiemetics.
- Ondansetron
- Granisetron
- Tropiseteron
- Dolasetron
- Palonosetron
HMG Co-A reductase inhibitors : "-statin"
Statins are the well known drugs that decrease LDL cholesterol and increase HDL cholesterol. They inhibit one of the key enzyme in the biosynthesis of cholesterol i.e. HMG Co-A reductase.
- Simvastatin
- Lovastatin
- Atorvastatin
- Rosuvastatin
- Pravastatin
Campothecins : "-tecan"
Campothecins are the natural products that inhibit topoisomerase I and used as anticancer agents.
- Topotecan
- Irinotecan
Thiazides : "-thiazide"
This is one class of diuretics having category name as their suffix. So we can easily identify by names ending with “-thiazide”. These drugs used in hypertension and mild edema to decrease the body volume.
Examples:
- Chlorothiazide
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Bendroflumethiazide
Macrolides : "-thromycin"
Macrolides are a group of large molecules that inhibit protein synthesis by inhibiting translocation. These drug names end with suffix “-thromycin” which should not be confused with “-mycin”, the latter mainly representing aminoglycoside antibiotics.

Examples:
- Erythromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Azithromycin
Telithromycin is a related drug classified as ketolide.
H2 antagonists : "-tidine"
H2 antagonists are mainly used as antiulcer agents that inhibit excess gastric acid secretion mainly mediated by histamine. These drugs end with suffix “-tidine”.
- Cimetidine
- Ranitidine
- Famotidine
- Nizatidine
5-HT1D agonists : "-triptan"
Migraine headache is a cranial vasodilatory response where 5-HT1D agonists comes in to the play. These drugs produce cranial vasoconstriction by activating 5-HT1D receptors within the CNS. This class of drugs commonly called as triptan drugs due to their suffix.
- Sumatriptan
- Rizatriptan
- Almotriptan
- Naratriptan
- Eletriptan
- Frovatriptan
- Zolmitriptan
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors : "-zolamide"
This category of diuretics mainly reduces osmotic pressure decreasing intracranial pressure and intraocular pressure. Their drug names end with “-zolamide”.
Examples:
- Acetazolamide
- Dorozolamide
Here is a video on how to remember drug names easily by using their unique suffixes for each category.
That's it. These are the 40 class of drug names having unique suffix and can be easily identified. We have summarised all these in a nut shell in the following picture.